The following article, allbeit long, provides a good overview of trade facilitation developments in Nigeria. I doubt that there is a single country on the African continent that cannot draw some parallel experience contained in this article.
Trade across borders is not a new phenomenon. But the World Trade Organization is now championing the concept of trade facilitation among nations, which has been defined as simplication , harmonization, standardization and modernization of trade procedures.
Trade facilitation seeks to reduce trade transaction between businesses and government. This concept is receiving unprecedented attention globally and it is at the heart of numerous initiatives within the customs world.
The United Nations Centre for Trade facilitation and Electronic business (UN/CEFACT) in its recommendation No 4 of 1974, said trade facilitation programme ought to be guided by simplication, harmonization and standardization (of trade procedures) so that transaction becomes easier, quicker and more economical than before.
According to the body, there was need to eliminate duplication in formalities, process and procedures; align all national formalities, procedures operation and documentation with international conventions, standard and practices to develop international agreed format for practices, procedures, documentation and information in international trade.
Proponent of trade facilitation believed that if transaction cost in international trade is reduced, there could be creation of wealth, especially in developing countries where red-tapism and other procedural barriers to trade tend to be pronounced.
The organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) estimated recently that even one per cent reduction in such “hidden cost” would boost the global economy by $40 billion with most of these benefits going to the developing world. Trade facilitation therefore encourages, or perhaps requires countries to adopt means such as publishing their imports and export procedures, reducing the number of forms that importers and exporters are required to complete, allowing forms to be submitted on-line, and checking corruption at border post.
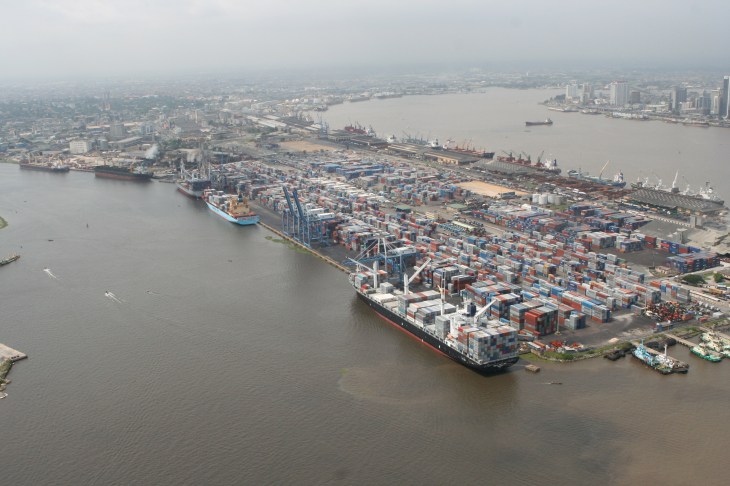
Nigeria, though a signatory to Kyoto 1974 and other convention on trade facilitation, is far from embracing the ideals of the global concept.
The president of the council of Managing Directors of Customs licensed Agents, Mr. Lucky Amiwero, said that although Nigeria was yet to comply with all the provisions of trade facilitation, it has the tools to facilitate international trade, such as the scanning machines and the e-platform.
“In Nigeria, the real cost of doing business is an impediment to trade facilitation. We have no good procedure for goods on transit to Niger and Chad. That has been taken over now by our neighboring countries. One of the key component of trade facilitation is charges which must be tied to services. We have shortcoming in that area. We are still working at cross purposes when other countries are busy harmonizing their import and export procedures”, he said.
In Nigeria, there is no one stop shop process for goods clearance as we have over 10 agencies superintending goods clearing procedure at the nation’s gateways.
“This is very bad and constitute hindrance to trade. The regulatory process is supposed to have been harmonized with other agencies to have a one stop procedures. Procedures are not published and not in line with WTO article which has to do with publication, regulation and administration of procedures. Our trading regime are expensive, our procedures are cumbersome. When others are simplifying and synchronizing their process of import and exports, our import and export procedures are lengthy. We have not been able to harmonise process and procedures and that is where we have a problem. If you still have to go through 100 per cent examination when we have the scanners, that is an impediment to trade,” Amiwero said; adding that the time spent to conclude business in Nigerian ports and border post is much higher than anywhere in the West African sub-region.
The level of corruption at the port border post is high and making them the most expensive business environment in Africa; as un-receipted charges far outweigh the official charges in the process of good clearing. Importers are still submitting hard documents instead of making use of e-devices, and going through the cumbersome process of clearing and receiving of consignments. Continue reading →
 Transport Forex, created by Inter Africa Bureau de Change, a registered bureau de change with the South African Reserve Bank has created an unique online banking system for the transport industry.
Transport Forex, created by Inter Africa Bureau de Change, a registered bureau de change with the South African Reserve Bank has created an unique online banking system for the transport industry.













You must be logged in to post a comment.