 I post this article given it ties together many of the initiatives which I have described in previous articles. The appears to be an urgency to implement these initiatives, but the real question concerns the sub-continent’s ability to entrench the principles and maintain continuity. At regional fora its too easy for foreign ministers, trade practitioners and the various global and financial lobbies to wax lyrical on these subjects. True there is an enormous amount of interest and ‘money’ waiting to be ploughed into such programs, yet sovereign states battle with dwindling skills levels and expertise. Its going to take a lot more than talk and money to bring this about.
I post this article given it ties together many of the initiatives which I have described in previous articles. The appears to be an urgency to implement these initiatives, but the real question concerns the sub-continent’s ability to entrench the principles and maintain continuity. At regional fora its too easy for foreign ministers, trade practitioners and the various global and financial lobbies to wax lyrical on these subjects. True there is an enormous amount of interest and ‘money’ waiting to be ploughed into such programs, yet sovereign states battle with dwindling skills levels and expertise. Its going to take a lot more than talk and money to bring this about.
South Africa is championing an ambitious integration and development agenda in Southern Africa in an attempt to advance what Trade and Industry Minister Rob Davies describes as trade and customs cooperation within the Southern African Customs Union (SACU), the Southern African Development Community (SADC) and other regional trade organisations.
Central to pursuing this intra-regional trade aspiration are a series of mechanisms to combine market integration and liberalisation efforts with physical cross-border infrastructure and spatial-development initiatives. Also envisaged is greater policy coordination to advance regional industrial value chains. “Trade facilitation can be broadly construed as interventions that include the provision of hard and soft infrastructure to facilitate the movement of goods, services and people across borders, with SACU remaining the anchor for wider integration in the region,” Davies explains.
This approach is also receiving support from the US Agency for International Development (USAid), which recently hosted the Southern African Trade Facilitation Conference, held in Johannesburg.
Trade programme manager Rick Gurley says that virtually every study on trade in sub- Saharan Africa identifies time and cost factors of exporting and importing as the most significant constraints to regional trade potential. Limited progress has been made by SADC member States and SACU partners to tackle the factors undermining trade-based growth, limiting product diversification and increasing the price of consumer goods, including of foodstuffs. However, far more would need to be done to realise the full potential of intra-regional trade.
Regional Alliance
One high-profile effort currently under way is the Tripartite Free Trade Area (T-FTA), which seeks to facilitate greater trade and investment harmonisation across the three existing regional economic communities of the SADC, the Common Market of Eastern and Southern Africa and the East African Community.
The existing SADC FTA should be fully implemented by the end of the year, with almost all tariff lines traded duty-free and, if established, the T-FTA will intergrate the markets of 26 countries with a combined population of nearly 600-million people and a collective gross domestic product (GDP) of $1-trillion. At that size and scale, the market would be more attractive to investors and could launch the continent on a development trajectory, Davies avers. It could also form the basis for a later Africa-wide FTA and a market of some $2.6-trillion.
However, as things stand today, intra- regional trade remains constrained not merely by trade restrictions but by a lack of cross-border infrastructure, as well as poor coordination and information sharing among border management agencies such as immigration, customs, police and agriculture.Cross-national connectivity between the customs management systems is also rare, often requiring the identical re-entry of customs declarations data at both sides of the border, causing costly and frustrating delays.
USAid’s regional economic growth project, the Southern African Trade Hub, is a strong proponent of the introduction of several modern trade-facilitation tools throughout the SADC – a number of which have already been successfully pioneered. These tools, endorsed by the World Customs Organisation (WCO) Framework of Standards, which offers international best-practice guidelines, are aimed at tackling the high costs of exporting and importing goods to, from, and within Southern Africa, which has become a feature of regional trade and discouraged international investment.
Bringing up the Rear
A country’s competitiveness and the effec- tiveness of its trade facilitation regime are measured by its ranking on World Bank indices and, with the exception of Mozambique, Southern African States perform poorly – with most in the region settling into the lowest global quartile of between 136 and 164, out of a total of 183. “Our transaction costs in Africa across its borders are unacceptably high and inhibit trade by our partners in the private sector,” says WCO capacity building director Erich Kieck. “We need our States to develop good ideas and policies, but the true test lies in their ability to implement them,” he notes.
He adds that not only does trade facilitation require efficient customs-to-customs connectivity, but also demands effective customs-to-business engagement, adding that, while customs units are responsible for international trade administration, they are not responsible for international trade. “The private sector is the driver of economic activity and international trade, and government’s responsibility is to understand the challenges faced by the business community and develop symbiotic solutions,” Kieck notes.
Despite the establishment of regional trade agreements and regional economic communities in Southern Africa, many partner- ships have failed to deliver on their full potential to increase domestic competitiveness.
In a report, African Development Bank (AfDB) senior planning economist Habiba Ben Barka observes that, despite the continent’s positive GDP growth record – averaging 5.4% a year between 2005 and 2010 – it has failed to improve its trading position or integration into world markets. In 2009, Africa’s contribution to global trade stood at just under 3%, compared with nearly 6% for Latin America and a significant 28% for Asia.
“Since 2000, a new pattern of trade for the continent has begun to take centre stage, as Africa has witnessed an upsurge in its trade with the emerging Brazil, Russia, India and China economies. Overall, Africa is trading more today than in the past, but that trade is more with the outside world than internally,” says Ben Barka. She adds that while many African regional economic communities have made some progress in the area of trade facilitation, much greater effort is required to harmonise and integrate sub-regional markets.
To address enduring trade barriers, consensus among business, government and trade regulators appears to lean towards the adoption of one or a combination of five facilitation tools. These include the National Single Window (NSW), the One-Stop Border Post (OSBP), cloud-based Customs Connectivity, Coordinated Border Management (CBM) and Customs Modernisation Tools.
A National Single Window
NSWs connect trade-related stakeholders within a country through a single electronic-data information-exchange platform, related to cross-border trade, where parties involved in trade and transport lodge standardised trade-related information or documents to be submitted once at a single entry point to fulfil all import, export and transit-related regulatory requirements.Mauritius was the first SADC country to implement the NSW and consequently improved its ranking on the ‘Trading Across Borders Index’ to 21 – the highest in Africa. It was closely followed by Ghana and Mozambique, which have also reported strong improvements.
Developed in Singapore, the benefits of government adoption include the reduction of delays, the accelerated clearance and release of goods, predictable application, improved application of resources and improved transparency, with several countries reporting marked improvement in trade facilitation indicators following the NSW implementation.
In South Africa, the work on trade facili-tation is led by the South African Revenue Service (SARS), which focuses on building information technology (IT) connectivity among the SACU member States, and strengthen- ing risk-management and enforcement measures. However, SARS’ approach to the NSW concept remains cautious, Davies explains. “SARS has considered the viability of this option as a possible technological support for measures to facilitate regional trade, but considers that this would fall outside the scope of its current approach and priorities in the region,” he said.
One-Stop Border Posts
As reported by Engineering News in December last year, effective OSBPs integrate the data, processes and workflows of all relevant border agencies of one country with those of another, which culminates in a standardised operating model that is predictable, trans- parent and convenient. An OSBD success story in Southern Africa is the Chirundu border post, where a collaboration between the Zambia and Zimbabwe governments has culminated in a single structure, allowing officers from both States to operate at the same location, while conducting exit and entry procedures for both countries.
Launched in 2009, this OSBP model is a hybrid of total separation, joint border operations and shared facilities in a common control zone. Implementation of the model has reduced clearance times to less than 24 hours, significantly reduced fraudulent and illegal cross-border activity, enabled increased information sharing between border agencies and reduced the overall cost of export and import activities in the area.
Earlier this year, former South African Transport Minister Sibusisu Ndebele indicated that Cabinet was looking into establishing a mechanism that would bring all border entities under a single command and control structure to address the fragmentation in the country’s border operations, particularly at the high-traffic Beitbridge post between South Africa and Zimbabwe. “The ultimate vision is to create one-stop border operations to facilitate legitimate trade and travel across the borders,” he said.
Customs Connectivity and Data Exchange
Improved connectivity between customs limbs in sub-Saharan Africa has perhaps made the most indelible strides in the region, with improved IT connectivity between States identified as a priority by Sacu.
This includes customs-to-customs inter- connectivity, customs-to-business inter- connectivity and interconnectivity between customs and other government agencies. SACU members have agreed to pursue the automation and interconnectivity of their customs IT systems to enable the timely electronic exchange of data between administrations in respect of cross-border movement of goods. “As a consequence of this acquiescence, we have identified two existing bilateral connectivity programmes as pilot projects to assess SACU’s preferred connectivity approach, cloud computing between Botswana and Namibia and IT connectivity between South Africa and Swaziland,” says SACU deputy director for trade facilitation Yusuf Daya. He adds that a regional workshop was recently convened to explore business processes, functions, data clusters and the application of infrastructure at national level to improve and develop intra-regional links.
Coordinated Border Management
The SADC has been a strong proponent of CBM efforts in the region, which promotes coordination and cooperation among relevant authorities and agencies involved in, specifically, the protection of interests of the State at borders. “The union has drafted CBM guidelines for its members on implementation, based on international best practice, and has received indications of interest from several member States,” explains SADC Customs Unit senior programme officer Willie Shumba.He adds that CBM is a key objective of regional integration, enabling the transition from an FTA to a customs union and, eventually, to a common market, through effective controls of the internal borders.
Customs Modernisation
South Africa’s customs modernisation initiative is well advanced and came about following Sars’ accession to the WCO’s revised Kyoto Convention in 2004, which required customs agencies to make significant changes to it business and processing models. These changes included the introduction of simplified procedures, which would have fundamental effects on and benefits for trade and would require a modern IT solution.
Since its inception, the SARS Customs Modernisation Programme has gained tremendous momentum, with amendments to the Passenger Processing System and the replacement of SARS’s Manifest Acquittal System in the Automated Cargo Management system. Further adjustments were made to enable greater ease of movement of goods, faster turnaround times and cost savings, as well as increased efficiency for SARS. This phase included the introduction of an electronic case-management system, electronic submission of supporting documents, the centralisation of back-end processing in four hubs and an electronic release system and measures to enhance the flow of trucks through borders – in particular at the Lebombo and Beitbridge borders.
Proper Planning
AfDB’s Ben Barka warns that, prior to the implementation of any border improvement efforts by countries in Southern Africa, a thorough analysis and mapping of each agency’s existing procedures, mandate and operations should be undertaken.“Based on these findings, a new set of joint operational procedures need to be agreed upon by all involved agencies and must comply with the highest international standards,” she says.
Development coordination between States is essential, as the largest disparity among regional groupings, in terms of intra-regional trade, is clearly attributable to their differentiated levels of progress in various areas, including the removal of tariffs and non-tariff barriers, the freedom of movement of persons across borders and the development of efficient infrastructure. Source: Engineering News.
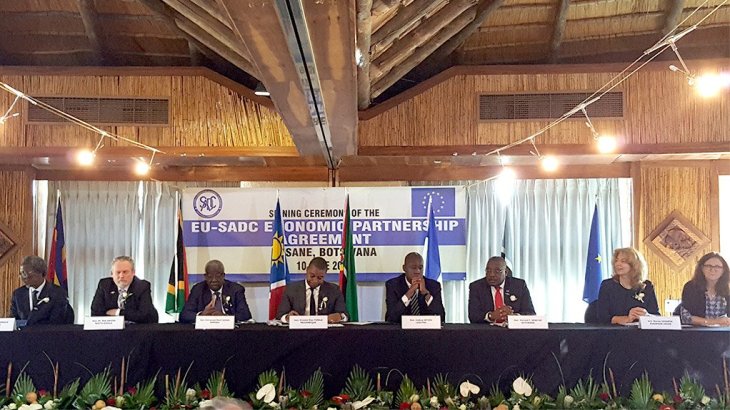 The EU has signed an Economic Partnership Agreement (EPA) on 10 June 2016 with the SADC EPA Group comprising Botswana, Lesotho, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa and Swaziland. Angola has an option to join the agreement in future.
The EU has signed an Economic Partnership Agreement (EPA) on 10 June 2016 with the SADC EPA Group comprising Botswana, Lesotho, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa and Swaziland. Angola has an option to join the agreement in future.

















You must be logged in to post a comment.