 Around 2008, most Southern African countries began to realise that the great ambition found on the SADC website at that time of moving from a SADC free trade area to a customs union by 2012 was not going to happen.
Around 2008, most Southern African countries began to realise that the great ambition found on the SADC website at that time of moving from a SADC free trade area to a customs union by 2012 was not going to happen.
The SADC website had a very EU-like regional integration agenda.
This is not surprising given that the great sugar daddy in Brussels basically funds the entire organisation. SADC wanted to replicate the EU linear model – first a free trade area where the countries trade freely among themselves; then a customs union where the members agree to a common tariff; and then a common market where all goods, services, capital and labour flow freely. Finally, SADC was to complete the copy of the EU by creating a monetary union.
This flattering imitation of the EU was obvious – the Brussels paymaster pays and we all happily follow their model into Kwame Nkrumah’s vision of a united Africa. But the ugly problem was, as ever, African history.
The less than subtle British also wanted a customs union in Africa. So, in 1910 they just created one – the Southern African Customs Union (SACU), which, like the proverbial bicycle without any pedals, still manages to stand because it is padded with money.
When the British implemented SACU after the Anglo-Boer War, there was no need for polite and time consuming subtleties of contemporary African consensus building. The Union of South Africa and the British high commissioner signed on behalf of the protectorates of Basutoland, Bechuanaland and Swaziland – not a black person in sight unless they were serving the tea.
Almost a century later those who designed the EU-like agenda for SADC’s integration conveniently forgot their history and somehow assumed that a customs union could be readily grafted on the SADC free trade area which was already in existence.
But there cannot be two external tariffs and, therefore, either SACU or SADC as a customs union had to go. And the difficulty that SADC faced with creating a customs union is that no one is ready to sacrifice national interests for a broader common good.
Free trade areas are relatively easy, they can be easily fudged, but customs unions are hard work because all the countries that are members have to agree to the external tariff.
In the meantime, the apartheid regime in Pretoria realised that it desperately needed to buy friends and influence enemies and so in 1969 it changed SACU from a regular customs union to one where the share of revenue from customs was derived from share of regional trade.
Normally, customs unions divide the revenue poll based on what economists call the ‘destination principle’. This meant that countries get the revenue depending on what imports were destined for that country. So if 5% of imports were destined for, say, Botswana, it would get 5% of the revenue.
But the SACU formula was purposely designed by South Africa to make the BLS (Botswana, Lesotho and Swaziland as members) completely dependent upon transfers from Pretoria by basing the formula on the share of intra-SACU trade and not external trade.
The oddity was that with the end of apartheid, things actually got even worse after the 2002 SACU re-negotiations because Pretoria agreed to a formula that made Botswana, Lesotho, Swaziland and newly independent Namibia get their share of customs revenue from SACU based on the share of intra-SACU imports.
SA imports almost nothing from SACU countries and the BLNS countries import almost everything from SA and so they get a huge amount of revenue. Many officials in Pretoria deeply resent the subsidies in SACU.
When the other SADC members saw how much money the BLNS countries were getting from Sacu, whenever the issue of a SADC customs union came up their response was – ‘me too please, we want the same formula!’
So, a SADC customs union would have eaten into the massive transfers (about N$20 billion per year) that Namibia and the rest of the BLNS states get each year from Pretoria and there was no way they were going to agree, and so the SADC customs union was not a realistic possibility.
After the obvious end of the SADC negotiations for a customs union, African negotiators began to look around for something that would keep them off the unemployment lines. The infamous African ‘spaghetti junction’ of the East African Community, Comesa and SADC with its overlapping membership became the next target. If you can’t form a customs union then just get a bigger FTA (free trade area).
Now this year, finally, an FTA has been signed but it has also been fudged. Few really want to give the highly competitive Egyptian producers free trade access to their African markets.
Ostensibly, we are moving to negotiate a continental free trade area which will finally begin the process of fulfilling of Nkrumah’s dream of a united Africa. But instead, what we have is Cecil John Rhodes’s dream of a market from Cape to Cairo – almost; no deepening of the African economic relationship into a customs union; just a widening to the north and west.
Free trade areas are a nice step forward but they normally require no real sacrifice of economic interests.
Europeans are guilty of many cruelties in Africa but none so absurd or spiteful as the ridiculous lines they drew on the map of the African continent in 1884 at the Berlin Conference when they divided up the continent. The Belgian barbarism in the Congo may fade from human memory and the wounds of apartheid may heal over time but African leaders will struggle to completely eliminate those economic and political lines from the map of Africa.
It is those lines and some petty “sovereign” economic interests that are the main reason why a billion dynamic people in Africa with such incredible natural resources continue to live in poverty. The Namibian (An opinion piece by Roman Grynberg, professor of economics at the University of Namibia.)


 Customs officers seized 31m counterfeit items at the EU’s borders last year worth more than €580m – with food, toys and cigarettes intercepted most frequently.
Customs officers seized 31m counterfeit items at the EU’s borders last year worth more than €580m – with food, toys and cigarettes intercepted most frequently.
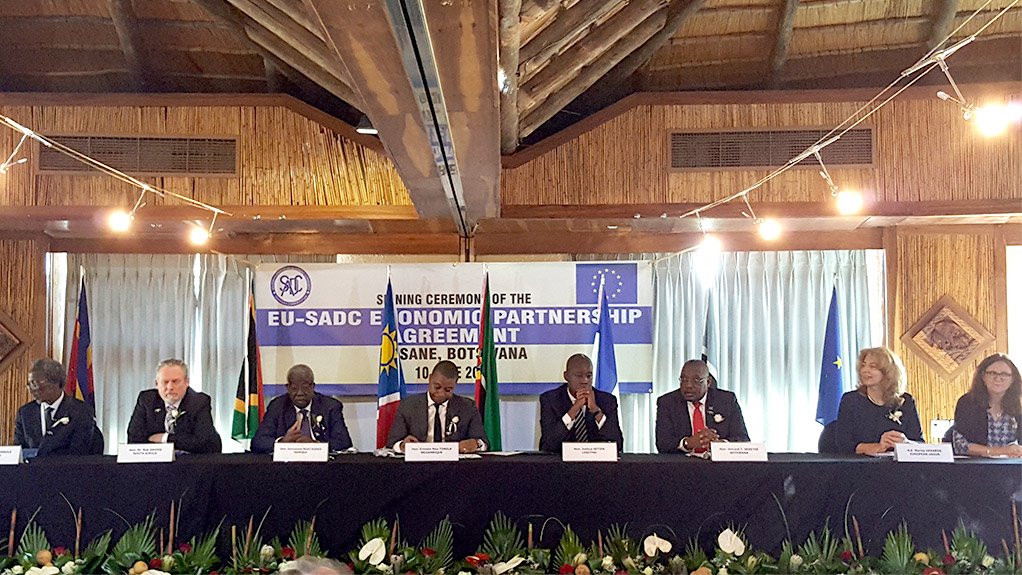 The EU has signed an Economic Partnership Agreement (EPA) on 10 June 2016 with the SADC EPA Group comprising Botswana, Lesotho, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa and Swaziland. Angola has an option to join the agreement in future.
The EU has signed an Economic Partnership Agreement (EPA) on 10 June 2016 with the SADC EPA Group comprising Botswana, Lesotho, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa and Swaziland. Angola has an option to join the agreement in future.
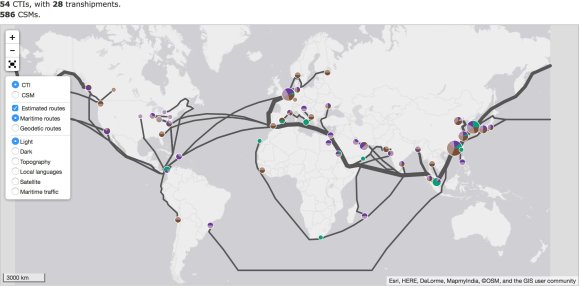 In collaboration with the European Anti-Fraud Office (OLAF), the JRC has worked extensively on how to exploit CSM data for customs anti-fraud purposes. The JRC proposed techniques, developed the necessary technology, and ran long-term experiments involving hundreds of EU customs officers to validate the usefulness of using CSM data. The results of this research led the Commission to bring forward a legislative proposal that would enable Member States and OLAF to systematically use CSM data for these anti-fraud purposes. It also served to convince Member States of the value of the proposed provisions.
In collaboration with the European Anti-Fraud Office (OLAF), the JRC has worked extensively on how to exploit CSM data for customs anti-fraud purposes. The JRC proposed techniques, developed the necessary technology, and ran long-term experiments involving hundreds of EU customs officers to validate the usefulness of using CSM data. The results of this research led the Commission to bring forward a legislative proposal that would enable Member States and OLAF to systematically use CSM data for these anti-fraud purposes. It also served to convince Member States of the value of the proposed provisions. The technologies, know-how and experience in handling CSM data, developed by the JRC through its experimental
The technologies, know-how and experience in handling CSM data, developed by the JRC through its experimental 







You must be logged in to post a comment.