
Secretary General of the WCO, Mr. Kunio Mikuriya, welcomes delegates to what is now one of WCO’s premium external events bringing together representatives of the software industry and Customs policy makers.
The 14th annual WCO IT Conference & Exhibition was officially opened on 6 May 2015 in Freeport (Bahamas). Senior Government representatives of The Bahamas Government opened the 3-day Conference in the presence of over 400 participants from 75 countries.
The Right Honorouble Perry Gladstone Christie, Prime Minister and Minister of Finance of the Commonwealth of The Bahamas thanked the WCO for choosing The Bahamas for this very important global Conference. The hosting of this WCO event is an example of the government’s commitment to bring business opportunities to Grand Bahama!
The Prime Minister further continued by reminding the delegates that the WTO concluded negotiations on a Trade Facilitation Agreement at the Bali Ministerial Conference in December 2013 and about its potential of reducing international trade costs of approximately 12%. He underlined that the WTO Trade Facilitation Agreement owes much to the technical work that had already been carried out at the World Customs Organization.
In his speech, the Prime Minister stressed: “Our efforts are very much consistent with the theme of this Conference “Inclusiveness Through Information Technology”. It is in our interest here in The Bahamas to pursue an inclusive approach to the introduction of the new IT systems. These new systems must bring benefits, not only to government, but also to commercial operators and to the general public who will use these services. We recognize that with the introduction of these IT systems we must adopt a more client focused and customer orientated approach to make it easier to conduct business.”
The Secretary General of the WCO, Mr. Kunio Mikuriya, welcomed the delegates to what is now one of WCO’s premium external events bringing together representatives of the software industry and Customs policy makers. The Secretary General emphasized the theme of this year’s Conference “Inclusiveness Through Information Technologies”, adding that it addresses three key priorities of the WCO Members – Implementation of the WTO Trade Facilitation Agreement, Regional Economic Integration and Coordinated Border Management.
Mr. Charles Turner, Comptroller of Customs and Excise Department of the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, stressed that the IT Conference & Exhibition comes at an important juncture for The Bahamas as the Customs Department implements the Trade Sector Support Program. Having such a broad range of exhibitors and international delegates provides a rare opportunity to share ideas and learn from the experiences of others. Source: WCO


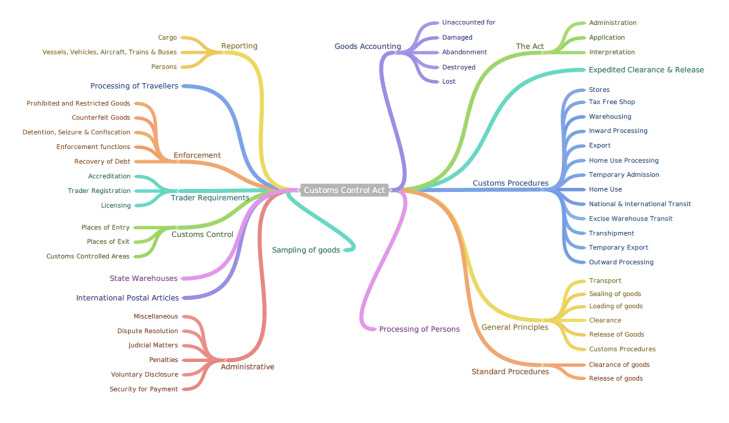
 As Customs and Border regulatory authorities ramp up their commitment to international agreements, such as the WCO Revised Kyoto Convention, SAFE Framework of Standards and the more recent WTO Trade Facilitation Agreement, more countries will offer a single point of entry through which traders, international carriers and logistics providers can access and comply with the resident customs and other government regulatory regimes.
As Customs and Border regulatory authorities ramp up their commitment to international agreements, such as the WCO Revised Kyoto Convention, SAFE Framework of Standards and the more recent WTO Trade Facilitation Agreement, more countries will offer a single point of entry through which traders, international carriers and logistics providers can access and comply with the resident customs and other government regulatory regimes. The Kenya Trade Network Agency, operator of the National Electronic Single Window System, has refuted claims by some clearing agents that the platform is lapsing.
The Kenya Trade Network Agency, operator of the National Electronic Single Window System, has refuted claims by some clearing agents that the platform is lapsing. 









You must be logged in to post a comment.