Having recently introduced a whole new integrated customs business solution last year the South African Revenue Service (SARS) has spent the last six months stabilising its system. At the heart of the system is the Interfront Customs and Border management (iCBS) engine which takes care of all customs declaration processing.
A new ‘state-of-the-art’ EDI Gateway infrastructure is at an advanced stage of development and configuration, and will be subjected to a series of rigorous testing both internally and with industry service providers over the next few weeks. The gateway is an important component of the organisation’s future aspirations in C-2-C, C-2-B and C-2-G information exchange with it’s stakeholders.
Over the last 2 years, SARS has been a key participant in the WCO’s Globally Networked Customs (GNC) initiative which seeks to develop standardised electronic information exchanges of commercial customs data and common border procedures between customs administrations. This is ‘greenfield development’ and requires innovative thinking between potential customs partners. In this specific area SARS has engaged both Mozambique and Swaziland Customs as willing partners in such an initiative. Developments with Mozambique are at an advanced stage and will shortly become a reality with the conclusion of the bilateral One Stop Border Post (OSBP) agreement that includes provision for electronic data exchange between the two administrations. More on this in a future post.
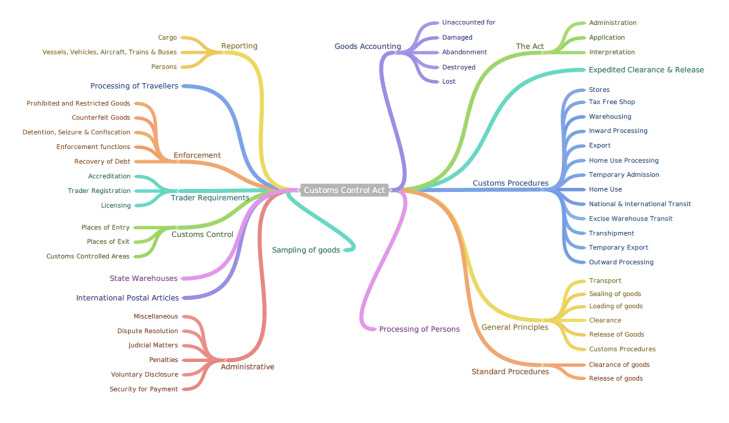
Technology aside, perhaps the most daunting task on the horizon is the introduction of the new Customs Duty and Control Acts which are currently in the parliamentary process. Much publicity and robust argument was aired in the printed media over the last year, all of which culminated in the parliamentary hearings overseen by parliament’s Standing Committee on Finance (SCoF) during November and December 2013. While an agreement was reached with the freight forwarding sector of the local supply chain and logistics industry on certain aspects of the Control Bill, there still lies much work and clarification to be addressed in these and other areas.
Notwithstanding the signing into law of the Customs Bills, operational enactment thereof can only occur once the ‘rules’ to execute this legislation are circulated for comment, finalised and gazetted. Even considering the legal and approvals process in a simplistic form, the implementation of this new legislation is just too complex to introduce in a once-off, big-bang approach. Due consideration must be given to a transitional approach taking into account the practicalities thereof as well as economic and logistical consequences of such approach. It is no understatement that the impact of the new legislation, its incorporation into current automated systems, policies and procedures as well as the necessary re-adjustments to be made by every entity engaged in business with SARS Customs is no small feat.
Furthermore, the implications of the recently concluded WTO Agreement on Trade Facilitation for South African Customs and Trade also needs to be determined and understood. While a large proportion of its content is encapsulated within the Revised Kyoto Convention, it is the first time ever that such requirements are subject to the conditions of a trade agreement.
It’s been some time since I last penned thoughts on the Customs Modernisation initiative. In retrospect and thinking ahead, the underlying bottom line to its longer term success lies in increased ‘communication’ with stakeholders – ironically, the World Customs Organisation’s adopted theme for 2014!
Please feel free to download the infogram on the future Customs Control Act by clicking on the picture above. Official links to the Customs Control and Duty Bills are included below. It would also be wise for parties involved in Excise to consider the contemplated changes contained in the Excise Duty Bill (Customs and Excise Amendment Bill).
Related documents

![SARS Customs North West Detector Dog Unit handlers. [SARS]](https://mpoverello.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/02/ddu_snapseed.jpg?w=730&h=505)











You must be logged in to post a comment.