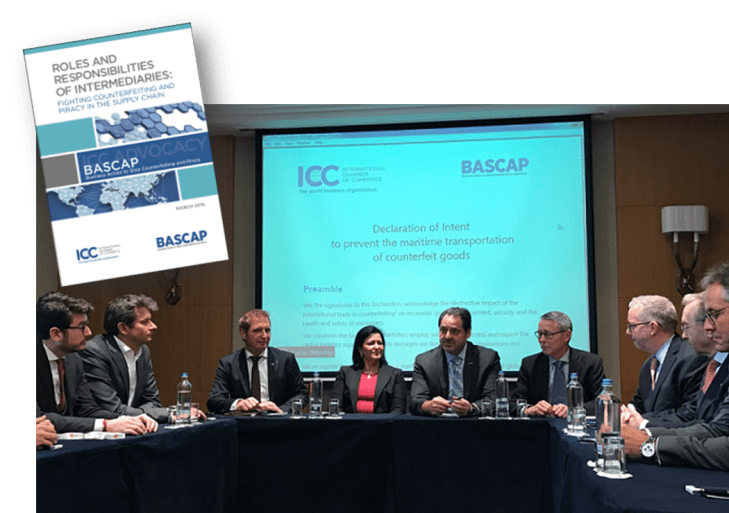

Leaders from global shipping firms, freight forwarders, brand owners whose products are counterfeited and industry organizations representing both industries signed a joint Declaration of Intent to Prevent the Maritime Transport of Counterfeit Goods in Brussels last week.
The event marked the first time the global shipping industry and brand owners have made a public commitment to work together to stop the transport of counterfeit goods on shipping vessels.
Initial signatories include the leading global shipping firms and freight forwarders and ten major multinational brand manufacturers, along with the International Federation of Freight Forwarders Associations (FIATA), and the International Chamber of Commerce’s (ICC) Business Action to Stop Counterfeiting and Piracy (BASCAP) and Commercial Crime Service (CCS).
More transporters, brand owners and their industry associations are expected to join the voluntary initiative as awareness grows.
According to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, about 90 percent of all international trade is moved around the world in more than 500 million containers on 89,000 maritime vessels. While this represents approximately 90 percent of all international trade, UNODC says that less than two percent of these containers are inspected to verify their contents. This results in enormous opportunities for criminal networks to abuse this critical supply chain channel to transport huge volumes of counterfeit products affecting virtually every product sector.
According to a recent OECD/EUIPO report, $461 billion in counterfeit goods moved through international trade in 2013, with almost 10 percent being shipped on maritime vessels.
Maersk Line and CMA CGM Group, two of the largest global transport companies with approximately half of all global shipping, and Kuehne and Nagel and Expeditors, two of the leading freight forwarding and logistics companies with total revenues of more than $27 billion, were the first in their industries to sign the Declaration.
The non-binding Declaration acknowledges the “destructive impact” of counterfeits on international trade. It calls on the maritime transport industry to address it “through continuous proactive measures, and corporate social responsibility principles.” The Declaration includes a zero tolerance policy on counterfeiting, strict supply chain controls and other due diligence checks to stop business cooperation with those suspected of dealing in the counterfeit trade.
This commitment paves the way for new voluntary collaboration programs between intermediaries and brand owners to stop abuse of the global supply chain by counterfeiters.
“We are proud to be among the first in our industry to sign this historic Declaration,” said Michael Jul Hansen, Customs and Trade Compliance Lead for Maersk Line. “Maersk has been a leader in taking steps to prevent the use of our vessels for the shipment of counterfeit and other illicit goods, and this Declaration is a reaffirmation of our intent to do everything we can to ensure our ships are counterfeit free.”
The Declaration is a direct reaction to the concerns of brand owners that vessels transporting their legitimate products were also being exploited by criminal networks to transport fake versions. This phenomenon was summarized in a landmark report on the Role and Responsibilities of Intermediaries: Fighting Counterfeiting and Piracy in the Supply Chain, published in 2015 by BASCAP. Following publication of the report, BASCAP organized a working group of its members to initiate a cross-sector dialogue with the transport industry to discuss ways to work together to find voluntary solutions. Source: Maritime Executive


 The National Regulator of Compulsory Specifications (NRCS), in its battle to protect the country from non-compliant goods whilst facilitating trade, advises that it intends rolling out a pilot programme aimed at cutting delays in the issuance of Letters of Authority (LOA).
The National Regulator of Compulsory Specifications (NRCS), in its battle to protect the country from non-compliant goods whilst facilitating trade, advises that it intends rolling out a pilot programme aimed at cutting delays in the issuance of Letters of Authority (LOA). Law firm Shepstone and Wylie cautions traders to be well aware of the legal considerations to be taken into account when negotiating an international trade transaction.
Law firm Shepstone and Wylie cautions traders to be well aware of the legal considerations to be taken into account when negotiating an international trade transaction.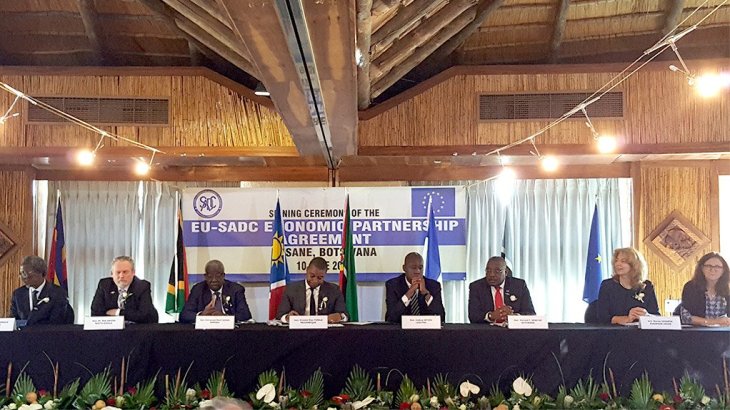 The EU has signed an Economic Partnership Agreement (EPA) on 10 June 2016 with the SADC EPA Group comprising Botswana, Lesotho, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa and Swaziland. Angola has an option to join the agreement in future.
The EU has signed an Economic Partnership Agreement (EPA) on 10 June 2016 with the SADC EPA Group comprising Botswana, Lesotho, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa and Swaziland. Angola has an option to join the agreement in future. Here follows an appreciation of AEO within the context of the EU. According to KGH customs consultancy services, being an Authorised Economic Operator (AEO) already entails advantages for companies that have invested in doing the work to gain the AEO certification. With the new Union Customs Code (UCC), companies with an AEO permit will be able to gain additional advantages leading to more predictable and efficient logistics flows as well as an increased competitive edge.
Here follows an appreciation of AEO within the context of the EU. According to KGH customs consultancy services, being an Authorised Economic Operator (AEO) already entails advantages for companies that have invested in doing the work to gain the AEO certification. With the new Union Customs Code (UCC), companies with an AEO permit will be able to gain additional advantages leading to more predictable and efficient logistics flows as well as an increased competitive edge. While commodity prices tanked and unemployment rose during South Africa’s worst ever drought over the last few months, wine making increased.
While commodity prices tanked and unemployment rose during South Africa’s worst ever drought over the last few months, wine making increased.
 The year 2015 has been the most active one ever for this joint WCO – UNODC initiative, which tackles illicit trade in containerized transport.
The year 2015 has been the most active one ever for this joint WCO – UNODC initiative, which tackles illicit trade in containerized transport.
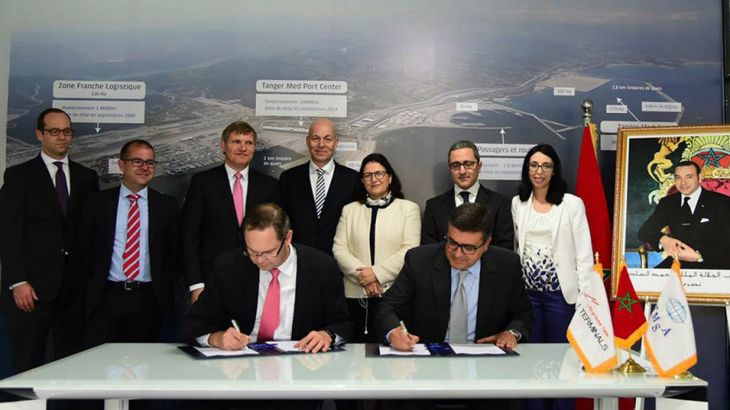
 Maritime Executive reports that the world’s third largest port operator APM Terminals said it will invest 758 million euros ($858.3 million) in a new transhipment terminal in Tangier, Morocco, that will be the first automated terminal in Africa.
Maritime Executive reports that the world’s third largest port operator APM Terminals said it will invest 758 million euros ($858.3 million) in a new transhipment terminal in Tangier, Morocco, that will be the first automated terminal in Africa. South Africa is moving away from a policy promoting trade and investment to one that contradicts this, a roundtable on SA-European Union (EU) trade relations heard on Tuesday.
South Africa is moving away from a policy promoting trade and investment to one that contradicts this, a roundtable on SA-European Union (EU) trade relations heard on Tuesday.
You must be logged in to post a comment.