
The Zimbabwe Herald suggests that Zimbabwe could be losing millions of dollars in unpaid taxes due to rampant smuggling of cigarettes into South Africa, investigations by this paper have revealed.Between 2014 and 2015, local customs officials seized nearly 2 500 cartons worth around $500 000 in taxes, according to the Zimbabwe Revenue Authority.
Figures from the South African side are staggering, showing a wide discrepancy in the value of confiscated contraband between the two neighbouring southern African countries.
The South African Revenue Service told The Herald Business that it had seized R87 million (US$6,2 million) worth of Zimbabwean cigarettes since 2014, or 95 million sticks.
This will likely be worth millions of dollars in evaded tax in Zimbabwe, but the ZIMRA director for legal and corporate services Ms Florence Jambwa said the figures were difficult to determine because smuggling was an underground trade.
South Africa, however, says it loses an estimated R40 million (US$2,9 million) to cigarette smuggling each year, on the average, more than half of it Zimbabwe-related.
And this is just from what is on public record. Customs officials from both countries admit the figures could be higher. Both are also greatly incapacitated to detect illegal trades quickly.
“It is difficult to measure the levels of smuggling as this is an underground activity mostly done through undesignated entry points,” said ZIMRA’s Jambwa, by email.
“The value of the potential loss cannot be easily ascertained,” she said, failing to provide an estimate.
Tax analyst Mr Tendai Mavhima said the figures from ZIMRA represent only a small portion of the actual amount of money Zimbabwe is losing to trafficking of cigarettes.
“The disparity in figures (ZIMRA and SARS figures) indicate there are problems in controls on either side, which may result in the revenue and tax losses from both countries being understated,” he said by telephone.
Zimbabwe is the world’s fifth largest producer of tobacco after China, the USA, Brazil and India.
The country produces flue-cured Virginia tobacco, considered to be of extremely high quality and flavour, according to a report on Zimbabwean tobacco companies by local stockbroking firm, IH Securities.
As such, Zimbabwean tobacco ends up in many top cigarette brands across the world, it says.
It is especially popular in China, the largest importer of Zimbabwean tobacco, and in South Africa, the country’s largest trading partner.
In South Africa, Zimbabwean cigarettes are on demand for two key reasons: high quality and affordability.
It costs just $1,50 for 20 sticks in Zimbabwe compared to $3,20 for the same number of sticks in South Africa, according to estimates by regional economic bloc, SADC.
The South African Revenue Service (SARS) said: “Cigarette clientele opt for cheaper cigarettes. The high supply and demand for illicit cigarettes creates the market for it.”
South Africa imposes very high taxes on cigarette imports – about 80 percent meaning many Zimbabwean dealers choose to export illegally.
SADC says illegal dealers supply nearly two thirds of the number of cigarettes smoked by South Africans.
In 2011 alone, at least 4 billion cigarettes smuggled into South Africa originated from Zimbabwe, it says.
The undeclared cigarettes are usually concealed in trucks, buses and other vehicles destined for South Africa by organised cartels, said Florence Jambwa of ZIMRA.
Sometimes the cargo is shipped at undesignated points on the porous border between the two countries. Source: Zimbabwe Herald








 As national Customs administrations and border agencies celebrate International Customs Day, no doubt showcasing their recent ICT endeavours, it is good to reflect not only on the available standards and tools which are becoming more available to Customs and Border Management Agencies.
As national Customs administrations and border agencies celebrate International Customs Day, no doubt showcasing their recent ICT endeavours, it is good to reflect not only on the available standards and tools which are becoming more available to Customs and Border Management Agencies. The WTO announced that the following countries have submitted their instruments of acceptance to the WTO Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA):
The WTO announced that the following countries have submitted their instruments of acceptance to the WTO Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA):

 Audit firm KPMG reports that the General Administration of Customs (GAC) will reform the existing customs clearance procedure for imported goods, according to a GAC Circular on Carrying out Pilot Reform of Tax Collection and Administration Procedure issued on 29 October 2016. Under the current procedure, review of the customs declaration is required before goods are released. This reform is designed to further guide import and export enterprises to be self-disciplined and law-abiding, with the principle stated as “honesty and observance of the law brings convenience; dishonesty and irregularity leads to punishment” to improve customs clearance efficiency.
Audit firm KPMG reports that the General Administration of Customs (GAC) will reform the existing customs clearance procedure for imported goods, according to a GAC Circular on Carrying out Pilot Reform of Tax Collection and Administration Procedure issued on 29 October 2016. Under the current procedure, review of the customs declaration is required before goods are released. This reform is designed to further guide import and export enterprises to be self-disciplined and law-abiding, with the principle stated as “honesty and observance of the law brings convenience; dishonesty and irregularity leads to punishment” to improve customs clearance efficiency.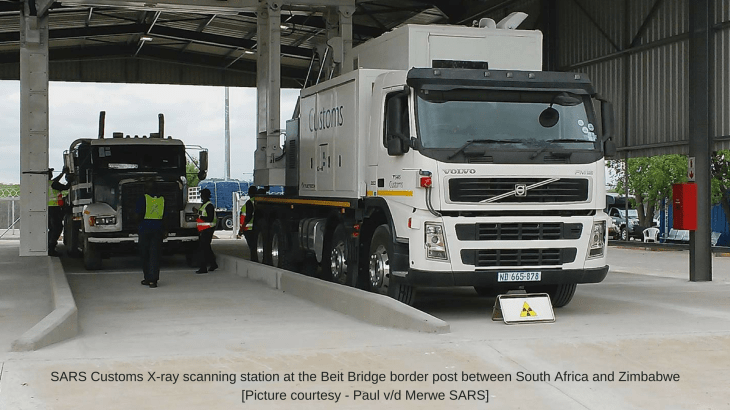



You must be logged in to post a comment.