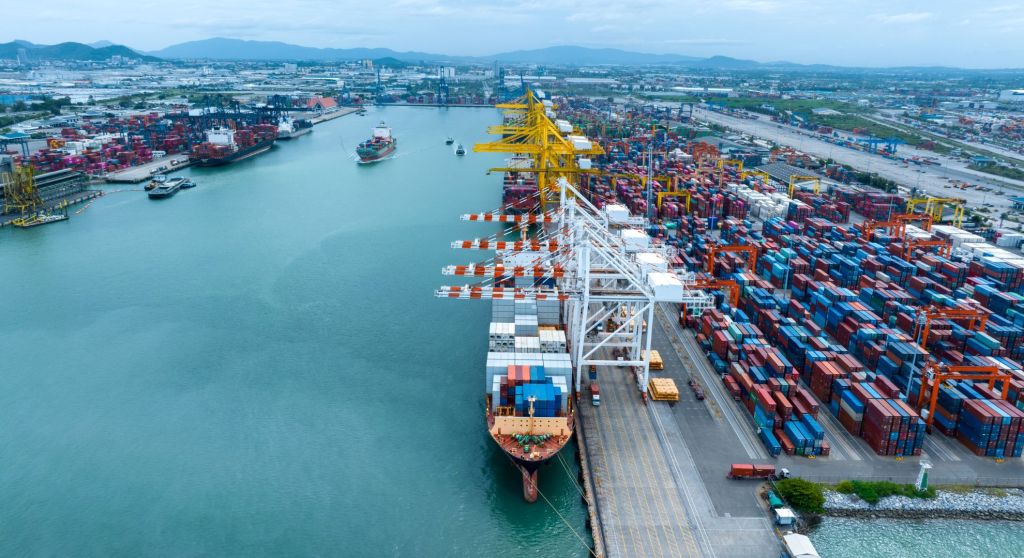

Mombasa port projects an increase in transshipment cargo after Kenya lifted the seven-year ban of stripping of cargo in containers at the port before onward delivery by dhows and barges to Zanzibar and Pemba.
The Kenya Revenue Authority (KRA) announced reintroduction of stripping, which is destuffing containerised cargo, after putting in place measures to curb smuggling, where before cargo is diverted in the ocean and finds its way into the East African Community (EAC) market.
The move is expected to cut the cost of container charges, considering that the boxes will be returned to the shipping line on time, since they will not be leaving the port as before.
Millers Association’s representative at the Mombasa port Naseeb Mbarak said the reintroduction of stripping would reduce the cost of transporting cargo to Zanzibar and Pemba by returning containers on time.
“Smaller traders will also benefit out of this as they can now import in groups,” he said. Mombasa-based clearing and forwarding agent Roy Mwanthi said the two destinations are the main transshipment destinations for Mombasa and the move will increase cargo numbers.
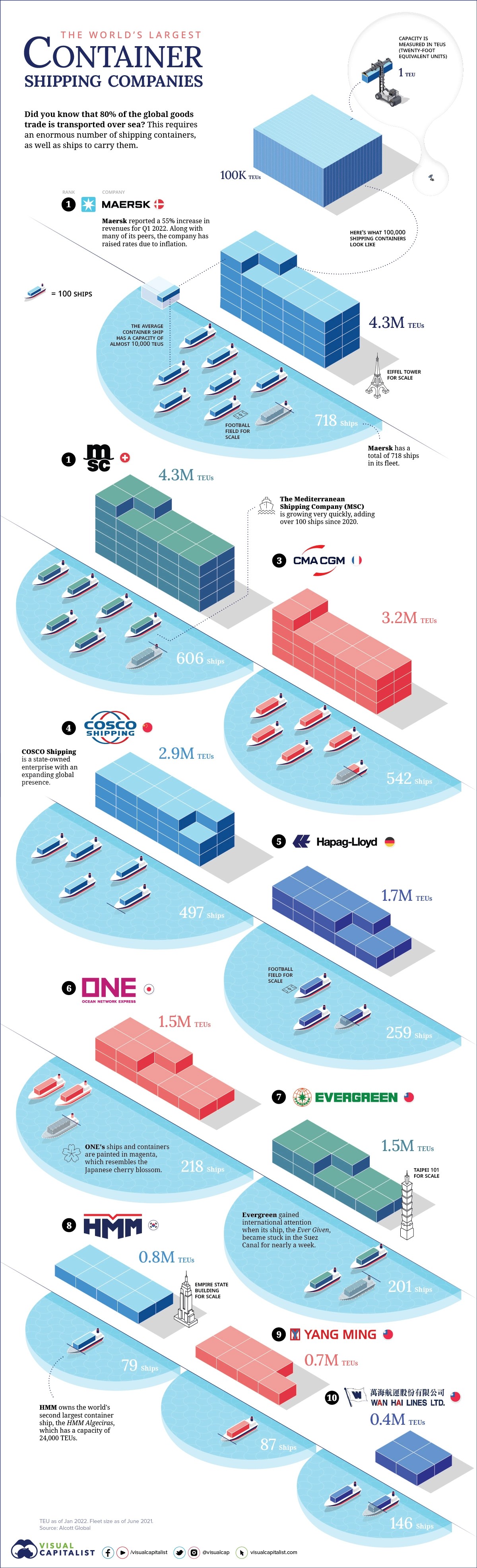
“Last year, Mombasa registered exceptional growth in transshipment traffic, which recorded 491,666 twenty-feet equivalent units (Teus), reflecting an extraordinary increase of 280,593 Teus and translating into 132.9 percent growth against 2023. With these numbers, stripping will surpass 500,000 units which will mean more Mombasa port revenues,” Mr Mwanthi said.
In 2018, the KRA in a public notice banned the stripping of containers destined for Zanzibar and Pemba. Before the ban, cargo destined for Zanzibar was being redirected to ports closer to the destination, such as Dar es Salaam, Tanga, or Zanzibar itself under a different manifest.
In November 2022, the Tanzania Revenue Authority (TRA) wrote to KRA requesting a review of the ban on stripping to facilitate their importers in Zanzibar and Pemba.
“KRA reviewed the same and granted indulgence on the stripping of cargo to Zanzibar and Pemba under conditions. In this regard, the earlier public notice issued is hereby set aside in line with this communication,” said the notice by KRA.
Before the ban, the volumes of cooking oil and other food stuff destined for Pemba and Zanzibar surpassed the consumption capacity of the two islands as a result of cargo diversion and smuggling.
KRA also seized different products, including edible oil cleared at Old Port in the go-downs of Mombasa, emanating from cargo stripped at the port of Mombasa.
To avert cargo diversion and control stripping, the KRA has prohibited changing the status of goods through manifest amendments.
The taxman said goods from the port of Mombasa have to be entered under the Single Customs Territory Framework (SCT) in Zanzibar before they are allowed into the islands.
“The shipments are to be cleared under SCT arrangement on duty paid basis and verified by TRA (Tanzania Revenue Authority) officers stationed in Mombasa before stripping and shipment. KRA enforcement to supervise stripping and loading of the cargo in the port before shipment,” read the notice dated April 8, 2025, and signed by customs officer Nicholas Ngeera.
Mr Ngeera said KRA will continue to liaise with the Kenya Ports Authority (KPA) to ensure that standard operating procedures and best practices on transshipment are implemented to protect and facilitate legitimate business.
Investigations by KRA and TRA show risks and challenges regarding transshipment cargo stripped at the port of Mombasa with increased cases of smuggling adversely Zanzibar islands and Pemba reported.
KRA also flagged med prolonged risks posed by stripping of cargo at the Port of Mombasa.
Last month, while in Mombasa, Zanzibar’s Minister of State in the President’s Office (Labour, Economy, and Investments), Sharif Ali Sharif, said delays in cargo delivery from Mombasa have historically caused shortages and price hikes in Zanzibar thus need to streamline transshipment process.
“Our cargo from China and the Middle East is first offloaded in Mombasa but, due to a lack of reliable transshipment, it often takes weeks or even months to reach Zanzibar. This has contributed to price increase for essential goods,” he said.
He said that the government had introduced tax exemptions and reductions on essential goods to keep prices reasonable.
With stripping of cargo reintroduced, Zanzibar expects a smoother supply of goods and ensures food security and price stability.
Source: The East African, article by Anthony Kitimo











You must be logged in to post a comment.